opsys-sp24
Operating Systems Spring 2024
Homework B - Processes
Q1 - State precisely in one sentence the effect and return value of the fork() system call in Unix.
Q2 - State precisely in one sentence the effect and return value of the execl() system call in Unix.
Now, the most common way of using fork and execl is this:
pid = fork();
if(pid==0) {
execl("program",...);
} else if(pid>0) {
wait(&status);
}
Which results in a single child process running “program”. This can be sketched as a process tree, like this:
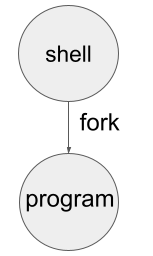
But there are many other ways to put the pieces together,
as shown below. Suppose that a program named “shell”
executes the following code snippets. (You may assume
that fork and execl always succeed in these examples.)
Q3 - Sketch a diagram showing the outcome of this program:
fork();
execl("program",...);
Q4 - Sketch the outcome of this program:
fork();
fork();
execl("program",...");
Q5 - Sketch the outcome of this program:
for(i=0;i<8;i++) {
pid = fork();
if(pid==0) {
execl("program",...):
}
}
Q6 - Sketch the outcome of this program: (notice the !=)
for(i=0;i<8;i++) {
pid = fork();
if(pid!=0) {
execl("program",...):
}
}
Q7 - Sketch the outcome of this program:
for(i=0;i<8;i++) {
fork();
}
execl("program",...):
Q8 - Sketch the outcome of this program:
for(i=0;i<8;i++) {
execl("program",...):
}
fork();